The Importance of Stem Cell Storage For Future Use
Stem cells have emerged as a cornerstone of modern medicine, offering potential treatments for various diseases and injuries. Their unique ability to regenerate and differentiate into various cell types makes them invaluable in research and therapy. However, one critical aspect often overlooked is the importance of stem cell storage. This article delves into what stem cell storage entails, its significance, methods, and future implications.
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unspecialized cells capable of dividing and developing into different cell types. There are two main types of stem cells:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Derived from early-stage embryos, these cells can differentiate into any cell type in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in various tissues, such as bone marrow, these cells help repair and regenerate specific tissues but have a more limited differentiation potential.
Understanding these cells is crucial when discussing their storage and applications.
Why is Stem Cell Storage Important?
1. Medical Advancements
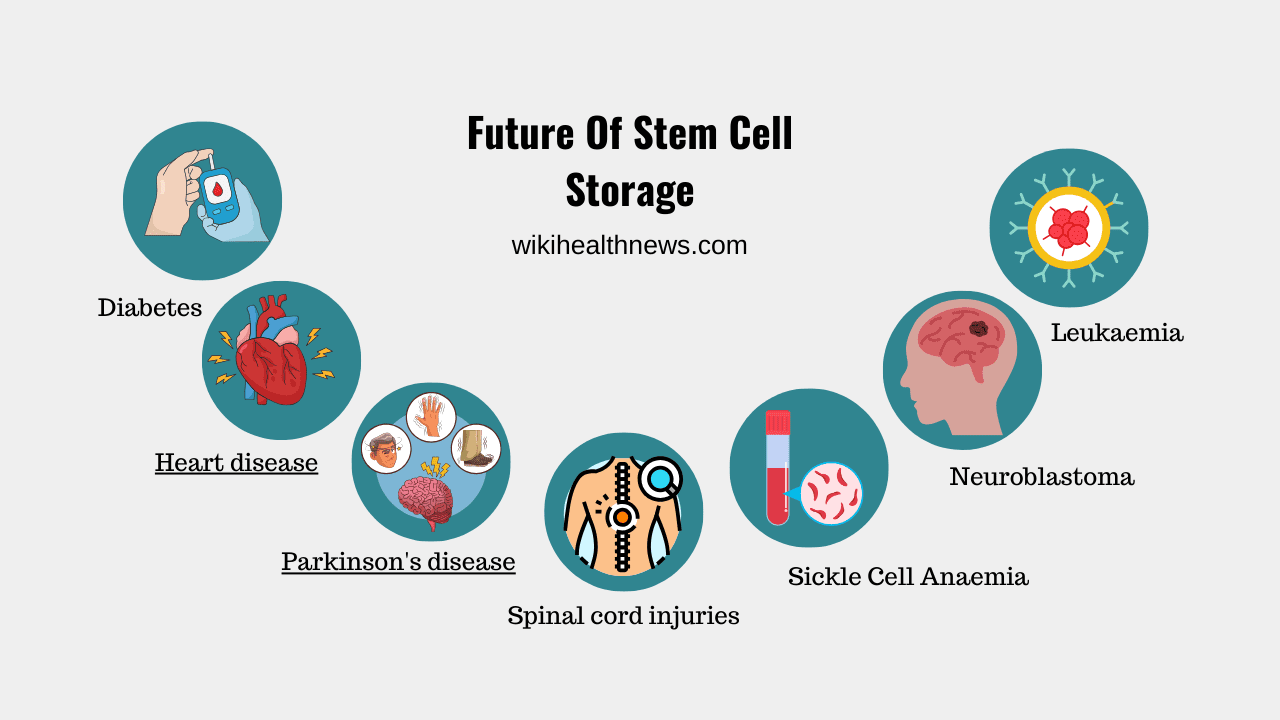
As research into regenerative medicine progresses, the need for readily available stem cells increases. They can potentially treat conditions such as:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease
- Spinal cord injuries
Storing stem cells ensures that they are available for future medical treatments and research, making them a valuable resource.
2. Personal Health Security
For individuals who have banked their stem cells, there is peace of mind knowing that they have access to their biological material should they need it in the future. This is particularly relevant for:
- Newborns: Many parents choose to store umbilical cord blood, which is rich in stem cells, for their child’s potential future health needs.
- Individuals with a family history of diseases: People at higher risk for certain conditions may choose to store their stem cells for potential therapies.
3. Research Opportunities
Stem cell storage facilities play a pivotal role in advancing scientific research. By providing researchers with access to diverse stem cell lines, they can study disease mechanisms and develop innovative therapies.
Methods of Stem Cell Storage
Stem cell storage involves several methods, primarily focusing on cryopreservation. This process requires careful handling to ensure the viability of the cells.
1. Cryopreservation
Cryopreservation is the most common method of storing stem cells. It involves cooling the cells to very low temperatures (typically below -150°C) to halt all biological activity, including metabolism and cell division.
- Process: The process begins with the collection of stem cells, followed by the addition of cryoprotectants to prevent ice crystal formation, which can damage the cells. The cells are then slowly cooled before being stored in liquid nitrogen tanks.
- Advantages: Cryopreservation effectively preserves cell viability and functionality, making it a reliable method for long-term storage.
2. Alternative Storage Methods
While cryopreservation is widely used, some alternative methods are being explored:
- Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying): This method involves removing water from the cells to create a powder form, making storage easier. However, it is less common for stem cells due to the sensitivity of these cells to the freeze-drying process.
- Storage in Bioreactors: Emerging technologies are looking into storing stem cells in bioreactors that can maintain optimal conditions for cell survival and growth.
Choosing a Stem Cell Bank
If you’re considering stem cell storage, choosing a reputable stem cell bank is essential. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Accreditation and Compliance
Ensure the bank is accredited by relevant authorities. This ensures that they follow strict guidelines and protocols for collection, processing, and storage.
2. Quality Assurance
Look for banks that implement quality control measures to maintain cell viability and integrity throughout the storage process.
3. Availability of Services
Choose a bank that offers comprehensive services, including collection, processing, storage, and potential future use of the stem cells.
4. Track Record
Research the bank’s history and success rates. Testimonials from clients and information on the bank’s experience can provide insight into their reliability.
Future Implications of Stem Cell Storage
As technology advances, the future of stem cell storage looks promising. Here are a few potential developments:
1. Personalized Medicine
With the rise of personalized medicine, stem cells may be tailored to individual patients, increasing the effectiveness of treatments. As storage methods become more efficient, the accessibility of these personalized therapies will improve.
2. Gene Editing
With advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, stored stem cells could be modified to correct genetic disorders before being reintroduced into the patient’s body.
3. Increased Research Opportunities
As more stem cells are stored, researchers will have a broader range of materials to study, potentially leading to breakthroughs in understanding and treating complex diseases.
Conclusion
Stem cell storage is an essential component of modern medicine and research. As the medical landscape evolves, the significance of preserving these unique cells will only grow. By understanding the methods, benefits, and future implications of stem cell storage, individuals can make informed decisions that may positively impact their health and the health of future generations.
Investing in stem cell storage not only safeguards personal health but also contributes to the ongoing journey of scientific discovery and innovation in regenerative medicine. Whether you’re considering banking your stem cells or simply interested in the field, being informed is the first step toward embracing the future of healthcare.
Read More