Appendicitis: An Emergency Condition
Appendicitis will happen when the appendix part is inflamed. This condition can be acute or chronic. Appendicitis is the most familiar cause of abdominal pain which results in surgery.
If appendicitis is left untreated it may cause the organ to burst by the inflammation. This burst will cause bacteria to spread in the abdomen cavity, which can be serious, and sometimes it causes death.
What is an appendix?
Appendix is a finger-shaped organ that attaches to the ileum on the lower right side of the abdomen.
Appendicitis also causes pain in the lower right abdomen. Here, in most people, the pain begins around the navel and then moves. As inflammation becomes severe appendicitis pain typically rises and eventually worsens.
Although anyone can develop appendicitis, more frequently it affects young people below 30 yrs. The most standard treatment is the surgical removal of the appendix.
Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis may include:
- Sudden pain will begin on the right side of the lower abdomen
- Sudden pain that starts around the navel and mostly shifts towards the lower right abdomen
- Pain that will become severe if you cough, walk or make other jarring movements
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Mild fever
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Abdominal bloating
- Indigestion
- Abdominal swelling
Appendicitis pain may start from mild cramping. It often becomes more steady and severe after time. It will start in the upper abdomen or belly button area, before moving to the lower right quadrant of the abdomen.
If appendicitis is suspected, then avoid taking laxatives or using an enema. These medicines will cause the severity of appendicitis or burst.
Consult with the doctor if you have these kinds of symptoms. Appendicitis will quickly become a medical emergency.
What causes appendicitis?
In many cases the main cause of appendicitis is unknown. Your doctor may suspect obstruction or blockage in some part of the appendix. Here many things can potentially block the appendix, including:
- Constipation
- Enlarged lymphoid follicles
- Intestinal worms
- Traumatic injury
- Tumors
When the appendix becomes blocked, bacteria can multiple inside the organs. This can also lead to the formation of pus and swelling, which can cause painful pressure in the abdomen.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
All with appendicitis do not have similar symptoms, and can be difficult at times to diagnose. Sometimes, the pain is not always located in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
Additionally, other conditions may also have similar symptoms, such as:
- Gastroenteritis
- Urinary tract infection
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Kidney stones
- Crohn’s disease
Here not every person has an appendix in the same place. Sometimes it is located behind the liver or the pelvis.
A doctor will examine the patients and ask some questions related to their symptoms. The doctor may apply some pressure to the area to check whether it worsens the pain.
Tests may include:
- Blood test, to check out for the infections.
- MRI, CT, and Total abdomen scan
- Urine test
Most likely, your doctors will make a decision to remove the appendix. Otherwise, it becomes too risky to wait for the test to confirm the diagnosis.
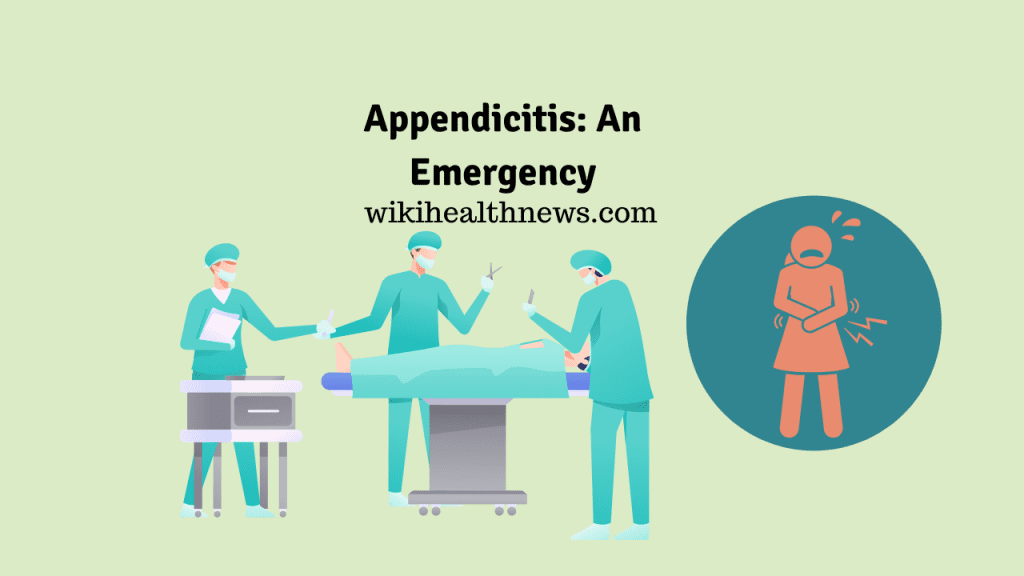
Treatment
Surgery
Mild infections will require only antibiotics to treat, but this is rare. In the majority of cases, a surgeon will remove the appendix. Often, this surgery is done through keyhole surgery or laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy:
Laparoscopic or minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves the following steps:
The surgeon inserts a very thin tube, or laparoscope, which has a small video camera. Through the scope or cannula light is focused into the abdomen for better visibility.
The surgeon will view the inside of the abdomen, through a monitor.
In laparoscopy, your doctor will use small surgical instruments responding to the movements of the surgeon’s hands. This will help remove the appendix through small abdominal incisions.
This is a precise operation, and there is a low loss of blood and a small incision. As a result, recovery time is faster than with open surgery, and there is low scarring.
Open surgery:
In some cases, laparoscopy may not be ideal. So, a larger incision is made to visualize the abdominal cavity and proper cleaning is done.
This will happens if:
- The appendix has ruptured, and the infection has spread
- The appendix has caused an abscess
- The patients have tumors in the digestive system
- For women in advanced stage of pregnancy
- The patients have had many abdominal surgeries before.
- After the surgery, the patient will be started on antibiotics intravenously.
What happens if you delay surgery?
If symptoms present at least for 5 days, the doctor may recommend a course of antibiotics to shrink the appendix and clear up the surrounding infection.
If there is an abscess, the doctors may drain it first and operate at a later date.
Antibiotics
Some antibiotics may give a safe and effective alternative for acute, uncomplicated appendicitis.
But surgery is more effective for appendicitis when compared to antibiotics.
Complications:
Appendicitis can cause serious main complications, such as:
A ruptured appendix:
A rupture will spread the infection throughout the abdomen (peritonitis). Consequently, it may cause a life-threatening condition. Thus, your surgeon will prefer immediate surgery to remove the appendix and clean the abdominal cavity.
A pouch full of pus that forms in the abdomen:
If the appendix bursts, it may develop a pocket of infection (abscess). In most cases, the surgeon will drain the abscess by placing a tube into the abdominal wall through the abscess. The tubes are left in place for about 2 weeks and given antibiotics to clear the infection.
Once the infection surpasses surgery can be done to remove the appendix. In some cases, the appendix is removed immediately once the abscess is drained.
Read more