Diabetes Health Screening: What are the tests?
Health Screening For Diabetes
Patients with diabetes often attend their whole health care checkup, either specifically for diabetes corresponding issues, or complications of their chronic illness, or for unrelated problems. It provides an annual assessment or checkup for either Type 1 or type 2 diabetes, focusing on the key role of risk factors from development of complications. Each visit can be viewed as an opportunity to assess and improve the patient’s understanding of their illness, and their ability to control the disease.
Why is an annual assessment important?
Patients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes should have a full body checkup or assessment once a year to ensure there is any damage to important body systems which may be caused by their diabetes.
What is the aim of assessing the patient with diabetes?
- To educate the patient on the importance of diabetes and to monitor and manage their diabetes as well as possible.
- To assess any problems in glycemic control and address them to improve diabetes.
- To find out any complications of diabetes and treat them.
- To educate and advise for healthy lifestyle modification.
- To assess the patient’s overall health and to treat any associated or coincidental illness, physically or mentally.
- To provide support and advice to the patients on how to manage with a chronic illness and how they can alter their lifestyle to maintain their health.
What tests are important for diabetes health screening?
HbA1C test:
The HbA1C test will measure the average blood sugar level over the past 2 or 3 months. An HbA1C below 5.7% is normal, between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates that they have prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher indicates that they have diabetes.
Fasting blood sugar test:
- This fasting blood sugar measures the blood sugar after overnight fasting (not eating).
- When your blood sugar level is 99mg/dL or lower in a fasting state it is termed normal.
- Prediabetes values are 100 to 125mg/dL
- High blood sugar values will show 126mg/dL or high.
Glucose tolerance test:
This measures the blood sugar before and after drinking a liquid which will have glucose. This test needs to collect the blood from fasting stomach overnight and need to check for blood glucose level. Then the person need to drink the liquid of glucose and have a blood sugar level to be checked for 1 hour, 2 hours, and possibly 3 hours after the glucose is drunken.
At 2 hours a blood sugar level of 140mg/dL or lower is consider normal.
Prediabetes range is 140 to 199mg/dL
Diabetes value is more than 200mg/dL.
Random blood sugar test:
This measures the blood sugar at the random time they tested. They can take this random blood sugar test at any time and this test doesn’t need any fasting.
In this test more than 200 mg/dL is having the diabetes.
The blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. They may have the urine test for ketones which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Tests for gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using the blood test. Here they tested between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Blood sugar that higher than normal early in pregnancy may indicate to have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
Glucose screening test
This measures the blood sugar at time when they are tested. They will give a liquid that contains glucose and then 1 hour later the blood will be taken and checked for blood sugar level. A normal result is 140 mg/dL or lower. If the level is higher than 140 mg/dL, then they need to check for a glucose tolerance test.
Other organ assessment in diabetes
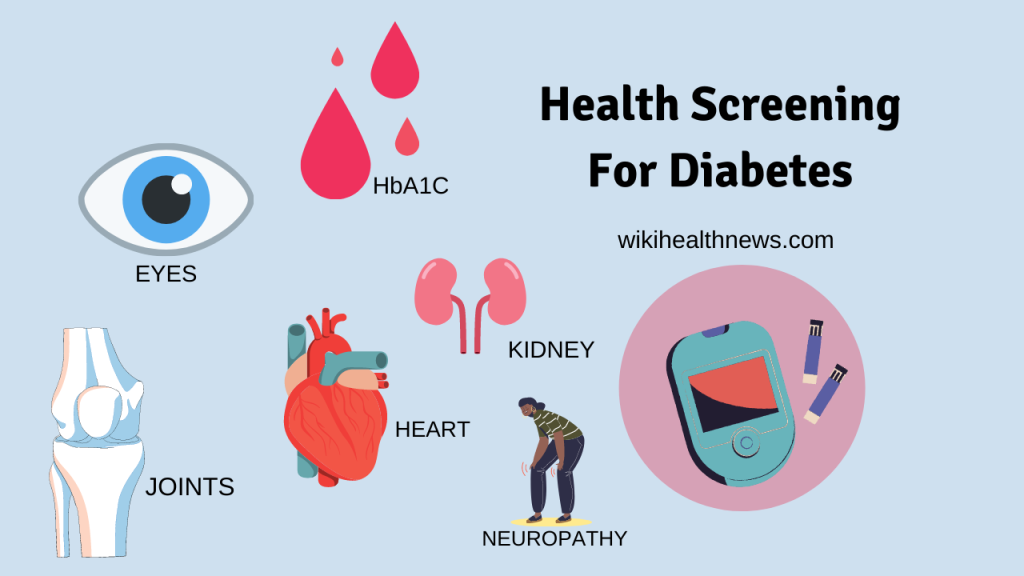
Eye examination:
- Visual acuity test
- Dilatation of the eye
- Retinal eye photography
- Visit ophthalmologist for retinal eye photography
Kidney function assessment:
- Blood sample
- Urine sample
Heart and blood pressure examination:
- Resting cardiograph
- Blood pressure
- Blood sample
- Weight, abdominal circumference, height and BMI need to be monitored regularly.
- Urinalysis for ketones, protein and nitrite.
Neuropathy:
- Examine the legs for evidence of diabetes amyotrophy.
- Check peripheral limb sensation eg. Using a 10g nylon monofilament probe.
- Examine ankle and knee reflexes using a tendon hammer.
- Inspect footwear and the feet carefully for any evidence of peripheral neuropathy causing deformity and ulceration, or hypo perfusion due to peripheral artery disease.
- Study of blood circulation in foot using a Doppler
- Visual assessment of the foot
Assessing and addressing modifiable risk factors:
- Glycemic control and how to improve it.
- Smoking habits and how to avoid smoking if needed.
- Dietary patterns
- Exercise and incorporate regular physical exertion
- Lifestyle modification
- Blood pressure need to be improved and control with medication
- Avoid weight gain or losing weight.
Read More