How to Prevent Gall Bladder Stones?
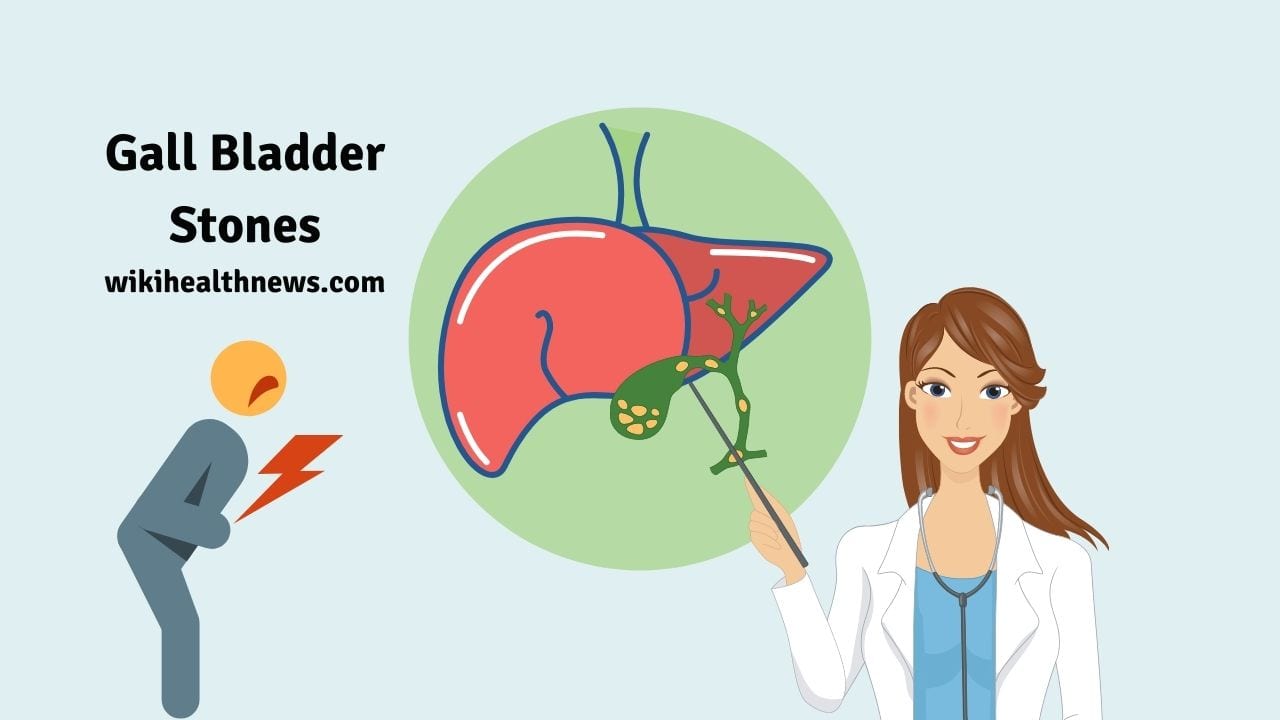
What are Gall bladder stones?
Gall bladder stones are long term deposits of bile in the gall bladder. This fluid is secreted from liver whenever there is need for digestion of food. The gall bladder is a small, pear shaped organ which is located in the right side of the abdomen, just below the liver. It holds the digestive fluid known as bile which is released to the intestines. It stores and releases bile into the gut for digestion of fat.
Gall stones vary in sizes and are without symptoms in many individuals. Mostly people who get symptoms are recommended to undergo surgery for gallbladder removal. Severe, unbearable pain is seen in advanced and complicated cases. It is more common in north americans and least among africans. Gallstones can vary in sizes. Some of us may develop only one gall stones where others may develop many gallstones at same time.
Types of stones:
Gallstones are made up of cholesterol, bilirubin, and calcium salts, with some protein and other material. They can be purely of one type or mixed stones containing more than one component. There are mainly 2 types of gallstones:
Cholesterol stones:
These are usually yellow green in color. This type of gallstone is mostly common, making up to 70-80% of gallstones cases.
Pigment stones:
These are very smaller and darker in color. They are made of bilirubin.
Mixed stones contain both these components in varying proportions.
Why gallstones appear?
These gallstones don’t have exact cause, but also may been happen:
There is too much cholesterol in bile:
The body needs bile for digestion. This bile usually dissolves cholesterol. But when the bile which is not dissolve these extra cholesterol may forms as a stone.
There is too much bilirubin in bile:
When people have infections, cirrhosis, and blood disorders can also cause liver to make more amount of bilirubin.
Gallbladder doesn’t empty all way:
This can also make bile very concentrated.
What are the symptoms of gall bladder stones?
Gallstones can present with pain in the upper right abdomen. The gall bladder pain will start from time of food taken which are high in fat. The pain will be severe in few hours of taken food.
Some common symptoms are:
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Dark color of urine
- Clay color stools, diarrhea
- Stomach pain & Indigestion problems
- Burping
- Pain in the right upper belly, and below the ribs.
- Pain in the right shoulder and backache
- Heartburns
These types of symptoms also called as billary colic.
Asymptomatic gallstones:
Gall stones mostly do not cause pain. But the pain will occurs if the gallstones block the flow of bile from the gallbladder. Mostly the gallbladder stone is known as silent gall stones. Which is won’t create pain or have symptoms. Mostly these cases are known by X-ray findings during abdomen surgery.
Who are at risk of gall bladder stones?
- Family history
- More than 40 years, Female have more chances
- Obese, Lack of exercise
- Diet in high fat and cholesterol but low in fiber
- Taking medicine for lower the cholesterol , Uses of hormone replacement therapy
- Diabetes, Intestinal disease like Crohn’s syndrome, Hemolytic anemia or cirrhosis of liver
- Taking fasting, Losing weight in short period
How to prevent gall stone formation?
Some lifestyle modification might lower the risk of gallstones. Few tips which can help to avoid formation of gall bladder stones:
- Do regular exercises
- Take high fiber diet, eat healthy food which is high in fiber and good fats, avoid refined carbohydrates, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Reduce starvation gap, avoid fasting
- Avoid long term use of certain drugs: Cholesterol lowering agents – clofibrate, antiulcer medicines – pantoprazole, certain antibiotics – ceftriaxone, contraceptive pills
- Don’t go for rapid weight loss program, avoid diet that makes lose of weight in short periods
- Maintain average weight: Obesity is a risk factor for gall stone formation.
What should I eat to avoid gallstones?
A western type of diet with high fat content, refined carbohydrates and low fiber content predisposes to gall stone formation. Diabetic diet with less sugar and more fat is also a risk factor. Since gall stone formation has a genetic basis it is better to avoid such diet if there is a family history. Coffee and milk seem to reduce the risk of stone formation. Prefer a diet containing more calcium and vitamin C.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis:
Some diagnosis which include:
Blood test: These blood investigation will check for the signs of infections or blockage, and rule out other conditions.
Ultra sound: This ultra sound makes images of inside of the organ.
CT scan: Specialized X-ray which physician can see clearly, including gallbladder.
Some other common Magnetic Resonance Cholangio Pancreatography(MRCP) which uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to make pictures of inside the organs.
Endoscopic ultrasound:
This is test which combines the ultrasound and endoscopy to view the gallstones.
What are the treatment for gall bladder stones?
There is no need of treatment if the symptoms don’t worsen. Some small sizes gallstones can pass through the organ by urine by own. Most people with gallstones have gallbladder surgery where the gallbladder is removed out. But the food will digest without gallbladder.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy:
This is the most common surgery for gallstones. The physician passes narrow tube called laparoscope into stomach through a small cut which holds instruments, light and camera. This is a small procedure where we can go some days after procedure.
Open cholecystectomy:
Here the doctor will cut bigger in the abdomen like open surgery and remove the gall bladder. Staying in the hospital is more compared to laparoscopy. If gallstones are in bile ducts, doctors may use ERCP to find the gallstone and remove before the surgery.
Some oral medication also given for dissolving the gallstones but it makes more years to destroy it.
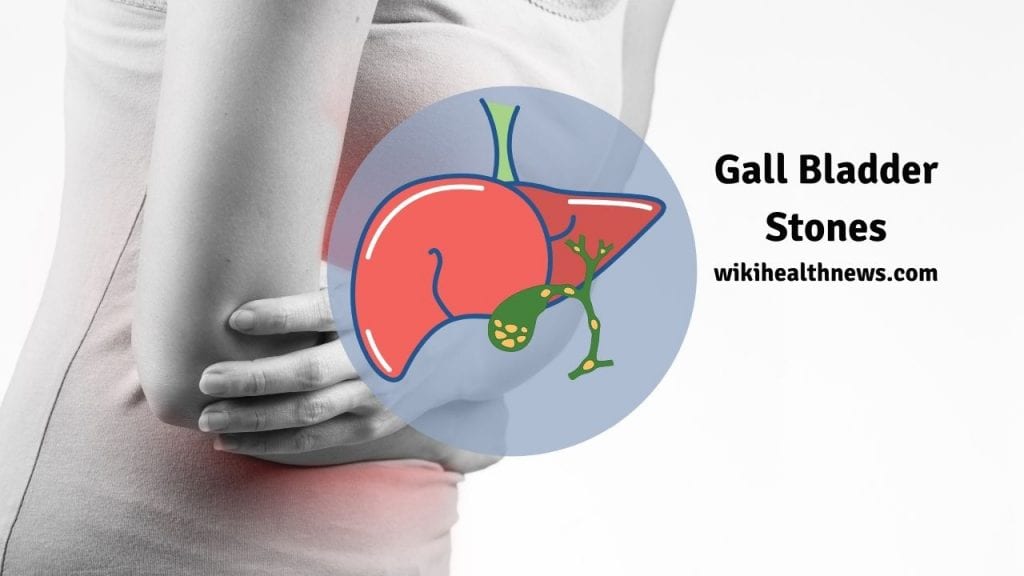
How serious are gallstones?
Gallstones will cause some serious complication which including:
Gall bladder inflammation:
This happens when a stone blocks the gallbladder so that is will not become empty. This situation will cause pain and fever. There is a situation where gallbladder might burst, if the treatment is delayed.
Blocked bile ducts:
This may also cause fever, chills and yellowing the skin and eyes. If the stones blocks duct of the pancreas the organ become inflamed.
Infected bile ducts:
A blocked duct is more quickly to get infected. If the bacteria is spread into bloodstream which is danger to the organs
Gallbladder cancer:
This is very rare but gallstones also raises the risk of kind of cancer may occur.
Read more